
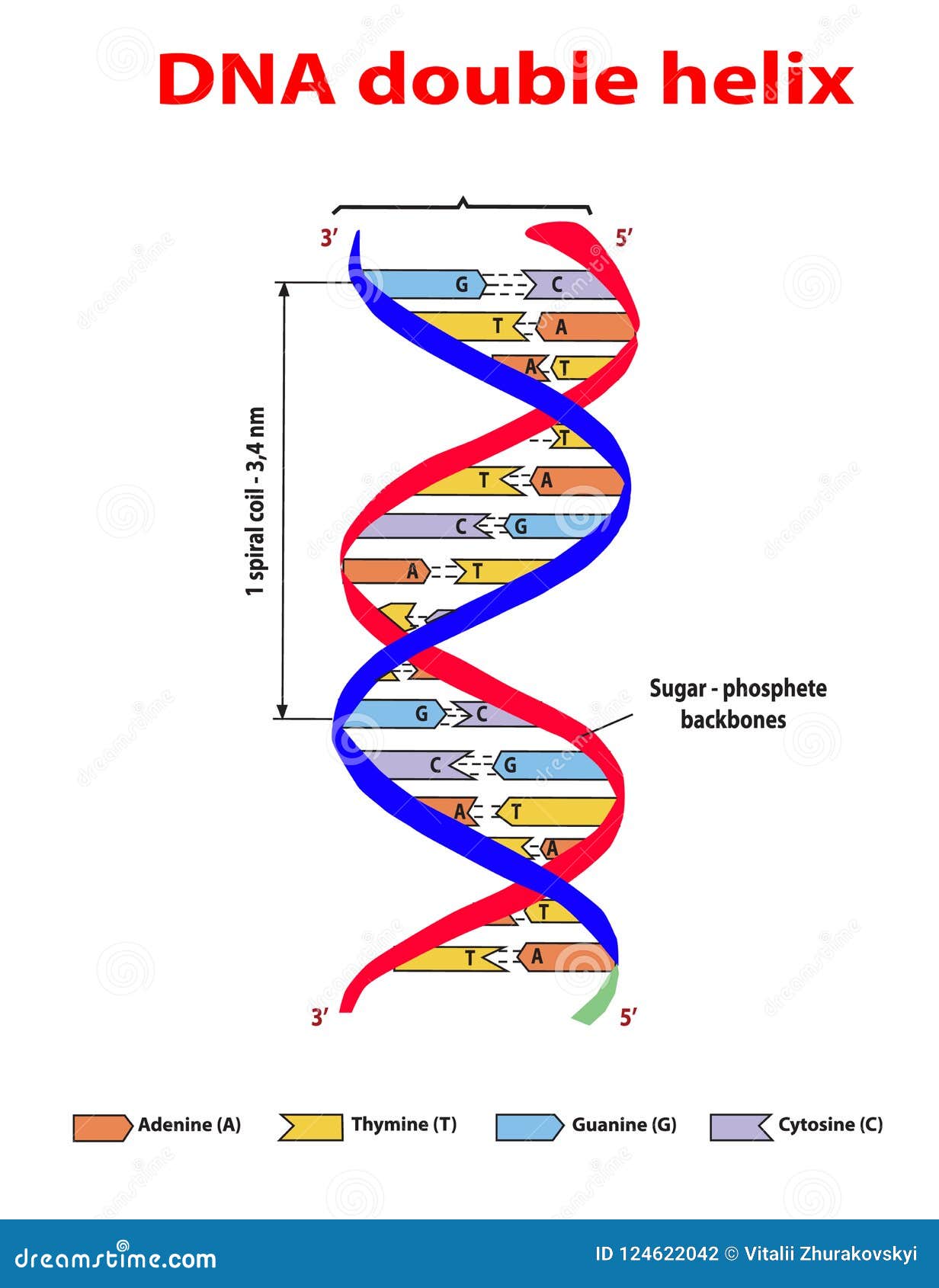
Unlike other duplexes, WC helix is unique by its ability to match the local energy minima of the free single strand to the preferable conformations of the duplex. No such sequence dependence exists in dDMPs corresponding to other DNA conformations (e.g., Z-family and Hoogsteen duplexes). Based on that, we infer that the directionality and the preferable regions of the sugar-phosphate torsions, combined with the difference of purines from pyrimidines in ring shape, determines the sequence dependence of the structure of WC DNA. by constructing Pyr-Pur from Pur-Pyr, and Pur-Pyr from Pyr-Pur sequences, while retaining the backbone geometry, automatically produces the mutual base position characteristic of the target sequence. Studying the conformational variability of dDMPs in response to sequence permutation, we found that simple replacement of bases in the previously fully optimized dDMPs, e.g. Geometry optimization of sugar-phosphate backbone produces energy minima matching the WC DNA conformations. In this work, we study the mechanisms of contribution of chemically monotonous sugar-phosphate backbone and the bases into the double helix irregularity. Our previous DFT computations of deoxydinucleoside monophosphate complexes with Na(+)-ions (dDMPs) have demonstrated that the main characteristics of Watson-Crick (WC) right-handed duplex families are predefined in the local energy minima of dDMPs. Poltev, Valeri Anisimov, Victor M Danilov, Victor I Garcia, Dolores Sanchez, Carolina Deriabina, Alexandra Gonzalez, Eduardo Rivas, Francisco Polteva, Nina The role of molecular structure of sugar-phosphate backbone and nucleic acid bases in the formation of single-stranded and double-stranded DNA structures. Detailed analysis of ionization products such as in DI is important to trace the sequential steps in the biochemical process of DNA damage. The threshold of this process is calculated to be 17.1 eV.

The DI cross section for the formation of H and (cytosine-Hl)(+), with the cytosine ion losing H at the 1 position, is also reported. Dissociative ionization (DI), a process that both ionizes and dissociates a molecule, is investigated for cytosine. The order is in accordance with the known propensity of oxidation of the bases by ionizing radiation. Of the four DNA bases, the ionization cross section of guanine is the largest, then in decreasing order, adenine, thymine, and cytosine. Furthermore, the sum of the ionization cross sections of the separate deoxyribose and phosphate fragments is in close agreement with the C3'- and C5'-deoxyribose-phospate cross sections, differing by less than 10%. It is found that the total ionization cross sections of C3'- and C5'-deoxyribose-phospate, two conformers of the sugar-phosphate backbone, are close to each other.

Fletcher, Graham D.Īs part of the database for building up a biochemical model of DNA radiation damage, electron impact ionization cross sections of sugar-phosphate backbone and DNA bases have been calculated using the improved binary-encounter dipole (iBED) model. Molecular Data for a Biochemical Model of DNA Radiation Damage: Electron Impact Ionization and Dissociative Ionization of DNA Bases and Sugar-Phosphate Backboneĭateo, Christopher E. Calculations are underway using a negatively charged sugar-phosphate backbone with a metal counter-ion. This allows us to obtain accurate properties of larger molecular systems built up from the results of smaller subsystem fragments. The result implies that certain properties of the- DNA, like the total singly ionization cross section, are localized properties and a building-up or additivity principle may apply. Furthermore, the sum of the ionization cross sections of the separate deoxyribose and phosphate fragments is in close agreement with the C3' - and C5" -deoxyribose-phospate cross sections, differing by less than 10%. Calculations using neutral fragments found that the total ionization cross sections of C3' - and C5', -deoxyribose-phospate, two conformers of the sugar-phosphate backbone, are close to each other. A64, 042719-1 (2001)l is used to study the total ionization cross sections of the DNA sugar-phosphate backbone by electron impact. The improved binary-encounter dipole (iBED) model [W.M. Electron-impact total ionization cross sections of DNA sugar-phosphate backbone and an additivity principle


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
